Ordenar coordenadas de latitud y longitud en cuadrilátero ordenado en el sentido de las agujas del reloj
Problema
Los usuarios pueden proporcionar hasta cuatro coordenadas de latitud y longitud, en cualquier orden. Lo hacen con Google Maps. Usando la API Polygon (v3) de Google, las coordenadas que seleccionen deben resaltar el área seleccionada entre las cuatro coordenadas.
Pregunta
¿Cómo ordenar una matriz de coordenadas de latitud y longitud en orden (contrario)a las agujas del reloj?
Soluciones y Búsquedas
StackOverflow Preguntas
- Dibujo de polígonos redimensionables (no intersectables)
- ¿Cómo ordenar los puntos en un polígono de Google maps para que las líneas no se crucen?
- Ordenar Cuatro Puntos en el Orden de las Agujas del Reloj
Relacionados Sitios
- http://www.daftlogic.com/projects-google-maps-area-calculator-tool.htm
- http://en.literateprograms.org/Quickhull_%28Javascript%29
- http://www.geocodezip.com/map-markers_ConvexHull_Polygon.asp
- http://softsurfer.com/Archive/algorithm_0103/algorithm_0103.htm
Algoritmos Conocidos
- El escaneo de Graham (demasiado complicado) [23] Jarvis March algoritmo (maneja N puntos)
- Casco convexo recursivo (elimina un punto)
Código
Esto es lo que tengo hasta ahora:
// Ensures the markers are sorted: NW, NE, SE, SW
function sortMarkers() {
var ns = markers.slice( 0 );
var ew = markers.slice( 0 );
ew.sort( function( a, b ) {
if( a.position.lat() < b.position.lat() ) {
return -1;
}
else if( a.position.lat() > b.position.lat() ) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
ns.sort( function( a, b ) {
if( a.position.lng() < b.position.lng() ) {
return -1;
}
else if( a.position.lng() > b.position.lng() ) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
var nw;
var ne;
var se;
var sw;
if( ew.indexOf( ns[0] ) > 1 ) {
nw = ns[0];
}
else {
ne = ns[0];
}
if( ew.indexOf( ns[1] ) > 1 ) {
nw = ns[1];
}
else {
ne = ns[1];
}
if( ew.indexOf( ns[2] ) > 1 ) {
sw = ns[2];
}
else {
se = ns[2];
}
if( ew.indexOf( ns[3] ) > 1 ) {
sw = ns[3];
}
else {
se = ns[3];
}
markers[0] = nw;
markers[1] = ne;
markers[2] = se;
markers[3] = sw;
}
Gracias.
3 answers
Dados los puntos:
4 + [d] [g]
|
3 [a] [e]
|
2 + [f] [h]
|
1 + [b]
|
0 +----+---[c]---+----+----+----+
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Usted quiere encontrar la siguiente caminata encuadernada:
4 + ___[d]------------[g]
| __/ \
3 [a]/ [e]__ \
| \ \_ ```--- \
2 + \ `[f] \___[h]
| \ __/
1 + [b] __/
| \ /
0 +----+--`[c]---+----+----+----+
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
?
Si esto es correcto, aquí hay una manera:
- encuentra el punto más alto, P top, en el conjunto de puntos. En caso de empate, elija el punto con la coordenada x más pequeña
- ordenar todos los puntos comparando las pendientes m i y mj de las líneas de cada par de puntos (excluyendo Ptop!) Pi and Pj make when pasando por P top
- si mi y mj son iguales, deje que el punto Pi o Pj más cercano a Ptop venir primero
- si mi es positivo y mj es negativo (o cero), Pj viene el primer
- si tanto m i como mj son positivos o negativos, que el punto perteneciente a la línea con la pendiente más grande sea primero
Aquí hay una demostración rápida para el mapa:
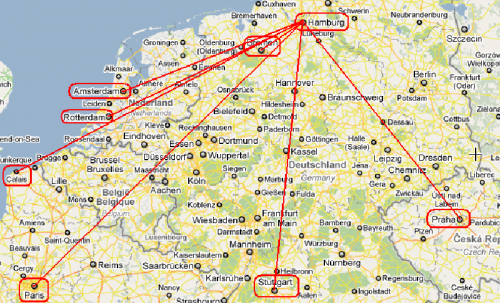
(Sé poco JavaScript, así que podría, o probablemente haya violado algunas convenciones de código JavaScript...):
var points = [
new Point("Stuttgard", 48.7771056, 9.1807688),
new Point("Rotterdam", 51.9226899, 4.4707867),
new Point("Paris", 48.8566667, 2.3509871),
new Point("Hamburg", 53.5538148, 9.9915752),
new Point("Praha", 50.0878114, 14.4204598),
new Point("Amsterdam", 52.3738007, 4.8909347),
new Point("Bremen", 53.074981, 8.807081),
new Point("Calais", 50.9580293, 1.8524129),
];
var upper = upperLeft(points);
print("points :: " + points);
print("upper :: " + upper);
points.sort(pointSort);
print("sorted :: " + points);
// A representation of a 2D Point.
function Point(label, lat, lon) {
this.label = label;
this.x = (lon + 180) * 360;
this.y = (lat + 90) * 180;
this.distance=function(that) {
var dX = that.x - this.x;
var dY = that.y - this.y;
return Math.sqrt((dX*dX) + (dY*dY));
}
this.slope=function(that) {
var dX = that.x - this.x;
var dY = that.y - this.y;
return dY / dX;
}
this.toString=function() {
return this.label;
}
}
// A custom sort function that sorts p1 and p2 based on their slope
// that is formed from the upper most point from the array of points.
function pointSort(p1, p2) {
// Exclude the 'upper' point from the sort (which should come first).
if(p1 == upper) return -1;
if(p2 == upper) return 1;
// Find the slopes of 'p1' and 'p2' when a line is
// drawn from those points through the 'upper' point.
var m1 = upper.slope(p1);
var m2 = upper.slope(p2);
// 'p1' and 'p2' are on the same line towards 'upper'.
if(m1 == m2) {
// The point closest to 'upper' will come first.
return p1.distance(upper) < p2.distance(upper) ? -1 : 1;
}
// If 'p1' is to the right of 'upper' and 'p2' is the the left.
if(m1 <= 0 && m2 > 0) return -1;
// If 'p1' is to the left of 'upper' and 'p2' is the the right.
if(m1 > 0 && m2 <= 0) return 1;
// It seems that both slopes are either positive, or negative.
return m1 > m2 ? -1 : 1;
}
// Find the upper most point. In case of a tie, get the left most point.
function upperLeft(points) {
var top = points[0];
for(var i = 1; i < points.length; i++) {
var temp = points[i];
if(temp.y > top.y || (temp.y == top.y && temp.x < top.x)) {
top = temp;
}
}
return top;
}
Nota: debería duplicar o triplicar las conversiones de lat,lon a x,y ya que soy un novato si se trata de SIG!!! Pero tal vez ni siquiera necesitas convertir nada. Si no lo hace, la función upperLeft podría devolver el punto más bajo en lugar del más alto, dependiendo de las ubicaciones de los puntos en cuestión. De nuevo: triple ¡comprueba estas suposiciones!
Cuando ejecuta el fragmento de código anterior, se imprime lo siguiente:
points :: Stuttgard,Rotterdam,Paris,Hamburg,Praha,Amsterdam,Bremen,Calais
upper :: Hamburg
sorted :: Hamburg,Praha,Stuttgard,Paris,Bremen,Calais,Rotterdam,Amsterdam
Función de Distancia Alterna
function distance(lat1, lng1, lat2, lng2) {
var R = 6371; // km
var dLat = (lat2-lat1).toRad();
var dLon = (lng2-lng1).toRad();
var a = Math.sin(dLat/2) * Math.sin(dLat/2) +
Math.cos(lat1.toRad()) * Math.cos(lat2.toRad()) *
Math.sin(dLon/2) * Math.sin(dLon/2);
var c = 2 * Math.atan2(Math.sqrt(a), Math.sqrt(1-a));
return R * c;
}
Warning: date(): Invalid date.timezone value 'Europe/Kyiv', we selected the timezone 'UTC' for now. in /var/www/agent_stack/data/www/ajaxhispano.com/template/agent.layouts/content.php on line 61
2012-04-19 07:38:10
Idea del algoritmo: promedia los cuatro puntos para obtener un punto dentro del polígono. Luego calcule el ángulo del rayo entre ese punto central y cada punto, usando funciones trigonométricas inversas, como se explica aquí. Luego ordenar por los ángulos. Eso debería darte un orden (contrario)a las agujas del reloj, dependiendo del orden de clasificación y lo que consideres "cero grados".
ACTUALIZAR: aquí hay un código. En su mayoría no probado, pero es la idea.
function sorted_points(points) {
points = points.slice(0); // copy the array, since sort() modifies it
var stringify_point = function(p) { return p.x + ',' + p.y; };
// finds a point in the interior of `pts`
var avg_points = function(pts) {
var x = 0;
y = 0;
for(i = 0; i < pts.length; i++) {
x += pts[i].x;
y += pts[i].y;
}
return {x: x/pts.length, y:y/pts.length};
}
var center = avg_points(points);
// calculate the angle between each point and the centerpoint, and sort by those angles
var angles = {};
for(i = 0; i < points.length; i++) {
angles[stringify_point(points[i])] = Math.atan(points[i].x - center.x, points[i].y - center.y);
}
points.sort(function(p1, p2) {
return angles[stringify_point(p1)] - angles[stringify_point(p2)];
});
return points;
}
Ordena los puntos (una matriz de objetos como {x: 1, y: 1}) en sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj.
Warning: date(): Invalid date.timezone value 'Europe/Kyiv', we selected the timezone 'UTC' for now. in /var/www/agent_stack/data/www/ajaxhispano.com/template/agent.layouts/content.php on line 61
2010-05-19 00:57:50
Para aquellos que llegan aquí con un problema similar un año después:
No estoy de acuerdo con el camino obligado de la respuesta elegida. No hay una solución singular para el orden incluso con una dirección de reloj dada. El casco convexo de las coordenadas dadas elimina los puntos e y f. Estos se pueden unir en cualquier lugar a lo largo del camino. Objetivamente, h, e, f, c se puede mejorar a h,f,e, c manteniendo la dirección del componente x consistente - en este caso, negativa.
El significado de esto hace imposible garantizar la inclusión de cualquier ubicación del mapa en el área resultante delimitada por la caminata elegida.
Warning: date(): Invalid date.timezone value 'Europe/Kyiv', we selected the timezone 'UTC' for now. in /var/www/agent_stack/data/www/ajaxhispano.com/template/agent.layouts/content.php on line 61
2011-08-05 14:29:19